As education systems continue to evolve, one of the primary goals remains ensuring that students are prepared for the challenges and opportunities that lie beyond high school, especially in the realms of college and career. A critical tool helping educators measure and guide student readiness for these next steps is the NWEA Measures of Academic Progress (MAP) test. The MAP assessment, which evaluates student growth in subjects like mathematics, reading, and language usage, is not only useful for tracking academic progress but also has a significant role in predicting and aligning with future college and career success.
Understanding the NWEA MAP Test
The NWEA MAP test is a computer-adaptive assessment that tailors the difficulty of questions to the student’s abilities. This means that as a student answers questions correctly, the test adjusts to become more difficult, and if they answer incorrectly, the questions become easier. The result is a personalized and accurate measure of a student’s academic level across different subjects, allowing educators to see exactly where a student stands relative to their grade level and beyond.
Unlike traditional standardized tests, which focus on specific content areas or grade-level expectations, MAP focuses on growth, providing a comprehensive picture of how much a student is learning over time. The test is typically administered several times a year, offering educators and parents a consistent way to track progress and address learning gaps.
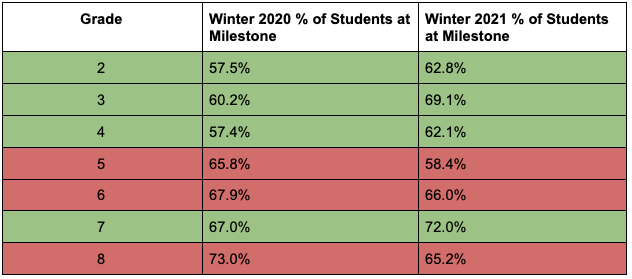
Aligning MAP with College and Career Readiness
College and career readiness is a key objective for educators and school systems worldwide. This concept generally refers to the knowledge, skills, and attributes that students need to succeed in postsecondary education or enter the workforce directly after graduation. The NWEA MAP test aligns with this goal by providing data that correlates strongly with future success in both academic and career environments.
MAP assessments are specifically designed to assess not just what students know, but how well they are progressing in areas critical to both college and career success. Research by NWEA shows a clear connection between map scores by grade level 2023 and performance in high school and beyond. For example, studies have indicated that students who score in higher percentiles on MAP tests are more likely to perform well on other college readiness indicators, such as the SAT, ACT, and Advanced Placement (AP) exams.
Predictive Power for College Success
One of the primary ways that NWEA MAP scores align with college readiness is through their predictive power for college success. Because the MAP test measures academic growth over time and tracks students’ progression in key academic areas, it provides insights into a student’s potential to succeed in more advanced coursework, which is a critical component of college preparation.
For instance, high MAP scores in math and reading can serve as an early indicator of a student’s preparedness for the rigorous coursework that college demands. Students who score well on MAP tests are more likely to complete challenging high school courses such as calculus, chemistry, and advanced English, which are often prerequisites for college admission. In this way, the MAP test serves as a reliable benchmark for assessing whether students are on track to meet the academic demands of higher education.
Additionally, MAP’s growth-centered approach helps identify students who may need additional support or acceleration before they enter college. By measuring growth in specific academic areas, educators can pinpoint areas where students are struggling and provide targeted interventions that ensure students are ready to meet college expectations.
Career Readiness and Real-World Skills
While much of the focus of MAP testing tends to be on academic performance, its role in career readiness is also significant. The skills tested on the MAP assessment—such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication—are foundational for many careers in today’s world. Whether students go on to attend college or enter the workforce directly, these skills will serve them well.
For example, in the workforce, employees are often required to use mathematics, analyze complex texts, and demonstrate problem-solving abilities. MAP tests measure exactly these types of competencies, which are highly transferable to careers in industries like engineering, technology, business, and healthcare. The MAP test provides a comprehensive picture of these foundational skills, allowing educators to ensure students are prepared for real-world challenges, whether in higher education or the job market.
Moreover, MAP data can help schools align their curricula with the skill sets employers are looking for. By looking at growth patterns and performance data across subjects, educators can adapt their teaching strategies to better prepare students for the demands of both college and the workforce. This helps ensure that students are not just academically ready, but also equipped with the practical skills needed to succeed in their future careers.
The Role of MAP in Personalized Learning
One of the most powerful aspects of the MAP test is its ability to support personalized learning. By measuring individual student growth and academic strengths and weaknesses, MAP enables educators to tailor instruction to each student’s specific needs. This approach is critical in ensuring that students develop the skills necessary for both college and career success.
For example, if a student consistently scores low in reading comprehension on MAP tests, educators can implement additional interventions, such as specialized tutoring or reading programs, to strengthen that skill. Likewise, students who demonstrate strong performance may be offered accelerated learning opportunities to further enhance their academic abilities.
Conclusion
The NWEA MAP test is much more than a tool for assessing academic performance—it is a powerful predictor of both college and career readiness. By tracking students’ academic growth in real-time, MAP offers valuable insights that allow educators, parents, and students to make informed decisions about educational interventions and future academic paths. The test’s ability to align with college and career success is built on its focus on measuring key competencies that will serve students well in higher education and in their future careers.
In today’s fast-paced and ever-changing world, it is more important than ever to ensure that students are not only prepared for their next grade level but also equipped to tackle the challenges they will face in college and the workforce. By leveraging the insights provided by MAP scores, educators can guide students on the path to success, ensuring they are ready to thrive in whatever their future holds.